1. 소개
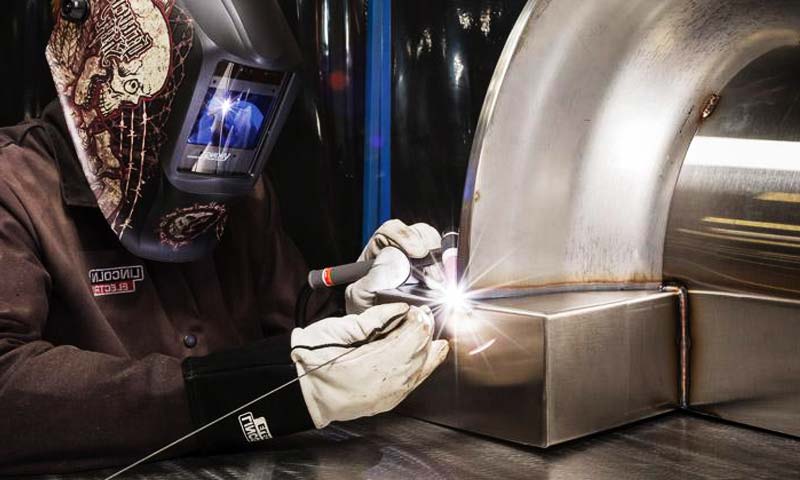
Laser cutting has emerged as a transformative technology in modern manufacturing, 비교할 수없는 정밀도의 조합을 제공합니다, 속도, 그리고 효율성.
Unlike conventional cutting methods that rely on mechanical force or abrasive tools, laser cutting employs a concentrated beam of light to slice through materials with exceptional accuracy.
Initially developed for industrial applications, laser cutting has expanded into various fields, 자동차 포함, 항공우주, 전자 제품, 의료, and even fashion.
오늘, it plays a crucial role in both prototyping and full-scale production, allowing manufacturers to create intricate designs with minimal waste.
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of laser cutting technology,
covering its fundamental principles, core techniques, 재료, 주요 응용 프로그램, 장점, 도전, 그리고 업계를 형성하는 미래의 추세.
2. Fundamentals of Laser Cutting
레이저 절단이란 무엇입니까??
레이저 절단 비접촉식입니다, thermal-based manufacturing process that utilizes a high-powered laser beam to cut or engrave materials.
The beam is directed through optics and guided by computer numerical control (CNC) systems to achieve precise, intricate cuts.
Compared to traditional cutting methods such as mechanical sawing or waterjet cutting, laser cutting offers significant advantages in terms of speed, 유연성, and accuracy.
It is widely used for processing metals, 플라스틱, 목재, 도예, 및 복합재, making it a versatile solution for various industries.
레이저 절단 작동 방식
The laser cutting process involves several key steps:
- Beam Generation – A laser source, such as a CO₂, fiber, or solid-state laser, generates an intense beam of light.
- Beam Focusing – Optical lenses and mirrors focus the laser beam to a precise point, increasing its energy density.
- Material Interaction – The concentrated laser beam heats, 녹는다, or vaporizes the material at the cutting point.
- Assist Gas Application – Inert or reactive gases (예를 들어, 질소, 산소) help remove molten material and enhance cutting efficiency.
- 모션 제어 – CNC systems guide the laser head along a predefined path, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
Key Components of a Laser Cutting System
A laser cutting machine consists of several critical components, each playing a specific role in ensuring precision and efficiency.
레이저 소스
The laser generator determines the power, wavelength, 응용 프로그램 적합성. 일반적인 유형은 다음과 같습니다.:
- Co₂ 레이저 – Ideal for cutting non-metals like plastics, 목재, and acrylic.
- 섬유 레이저 – Best for cutting metals such as aluminum, 스테인레스 스틸, 그리고 구리.
- Nd:YAG Lasers – Suitable for engraving and high-precision cutting.
Optical System
The optical system consists of mirrors and lenses that focus and direct the laser beam. 고품질 ZnSe (Zinc Selenide) lenses ensure minimal energy loss and improved cutting efficiency.
CNC 컨트롤러
에이 컴퓨터 수치 제어 (CNC) 체계 automates the laser movement, ensuring high-speed, high-precision cutting with repeatability.
Advanced CNC systems use AI-driven algorithms to optimize cutting paths, reducing material waste and production time.
Assist Gas Supply
Different gases are used to enhance the cutting process:
- 산소 (오 ₂): Increases speed for carbon steel but can cause oxidation.
- 질소 (n ₂): 깨끗합니다, oxidation-free cuts, commonly used for stainless steel and aluminum.
- Argon (AR): Prevents chemical reactions, ideal for titanium and specialty metals.
Motion System
The motion system includes motors and rails that move the laser head across the material. High-speed servo motors enable rapid acceleration and deceleration for faster processing speeds.
3. Types of Laser Cutting Technologies
The primary types of laser cutting technologies include CO₂ laser cutting, fiber laser cutting, Nd: YAG laser cutting, and ultrafast laser cutting.
Each technology has unique characteristics, making it suitable for different applications.
This section provides an in-depth analysis of these laser types, their working principles, 장점, 제한, 이상적인 사용 사례.
CO₂ Laser Cutting
CO₂ laser cutting is one of the most established laser cutting methods.
It utilizes a gas mixture of carbon dioxide (co₂), 질소 (n ₂), and helium (그) to generate a laser beam in the infrared spectrum (wavelength: 10.6 µm).
This wavelength is well-absorbed by non-metallic materials, making CO₂ lasers ideal for cutting plastics, 목재, 유리, 및 직물.

작업 원칙
- Gas Excitation: A high-voltage electrical discharge excites CO₂ molecules, producing laser light.
- Beam Focusing: The light is directed through mirrors and focused onto the material using a ZnSe (Zinc Selenide) lens.
- Material Interaction: The concentrated beam heats and vaporizes the material, while an assist gas (usually oxygen or nitrogen) removes debris.
주요 장점
- Highly effective for non-metals such as 목재, 아크릴, 가죽, 고무, and fabrics.
- 제공 a smooth edge finish, 후 처리의 필요성을 줄입니다.
- Capable of high cutting speeds, particularly for thin sheets.
제한
- Less effective for cutting metals unless specialized coatings or techniques are applied.
- Optical components, such as lenses and mirrors, require frequent cleaning and maintenance.
- CO₂ laser machines occupy a larger footprint compared to fiber laser systems.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- 절단 acrylic and wood for signage and furniture.
- 처리 textiles and leather in the fashion and upholstery industries.
- 조각 glass and other delicate materials for decorative purposes.
파이버 레이저 절단
Fiber laser cutting is a modern technology that uses an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as ytterbium to generate a high-intensity laser beam.
Unlike CO₂ lasers, fiber lasers operate at a wavelength of 1.06 µm, which is highly absorbed by metals, making them the preferred choice for cutting steel, 알류미늄, 그리고 구리.

작업 원칙
- Laser Generation: The laser is produced by a solid-state fiber-optic system rather than a gas-filled tube.
- Beam Transmission: The laser beam is guided through fiber-optic cables, eliminating the need for mirrors.
- Material Cutting: The high-intensity beam melts or vaporizes metal, with assist gases (nitrogen or oxygen) aiding in the process.
주요 장점
- Highly efficient for metal cutting, outperforming CO₂ lasers by up to 50% in productivity.
- Lower maintenance costs due to the absence of mirrors and moving parts.
- 소형 디자인, requiring less floor space than CO₂ laser systems.
- Higher energy efficiency, converting 35-50% of electrical energy into laser output, compared to CO₂ lasers, which achieve 10-15% 능률.
제한
- Less effective for non-metallic materials such as 목재, 아크릴, and glass due to absorption characteristics.
- Higher initial investment compared to CO₂ laser machines.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- 산업 metal cutting ~에 자동차, 항공우주, and shipbuilding 산업.
- 고정밀 machining of metal components for manufacturing.
- Production of electronic and medical devices requiring fine detail and accuracy.
Nd:YAG Laser Cutting (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet)
Nd: YAG lasers are solid-state lasers that produce a high-energy beam at a wavelength of 1.064 µm, similar to fiber lasers.
These lasers are particularly useful for cutting metals and certain ceramics 높은 정밀도로.

작업 원칙
- Energy Pumping: 에이 flash lamp or diode excites the Nd:YAG crystal, generating a laser beam.
- Beam Amplification: The laser passes through an optical resonator to increase its intensity.
- Material Cutting: The high-energy beam interacts with the workpiece, melting or vaporizing it.
주요 장점
- 적합합니다 high-precision micro-cutting, making it useful for medical and electronic applications.
- Works effectively with reflective metals, ~와 같은 금, 은, 및 알루미늄, without beam reflection issues.
- Capable of high pulse energy, 이상적입니다 welding and deep engraving.
제한
- Lower energy efficiency compared to fiber lasers, leading to higher power consumption.
- Less scalable for large-scale industrial applications.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- Micro-welding and precision cutting ~에 medical and aerospace industries.
- Engraving hard materials, 포함 도예, diamonds, and metals.
- Cutting thin foils and sheets ~에 electronics manufacturing.
Ultrafast Laser Cutting (Femtosecond & Picosecond Lasers)
Ultrafast lasers operate in the femtosecond (10⁻¹⁵ sec) and picosecond (10⁻¹² sec) 범위, 생산 extremely short pulses of light.
These lasers cut materials without generating heat, making them ideal for applications requiring ultra-high precision.

작업 원칙
- Pulse Generation: A series of ultrashort pulses deliver high peak power without excessive heat buildup.
- 재료 제거: 과정 ablates material at a molecular level, preventing thermal damage.
- 콜드 가공: Unlike traditional laser cutting, this method eliminates 열 영향 구역 (위험요소).
주요 장점
- Cold cutting process prevents thermal damage, making it suitable for delicate materials.
- Capable of sub-micron precision, 달성 nanometer-scale accuracy.
- Compatible with a wide range of materials, 포함 중합체, 유리, and bio-materials.
제한
- High cost due to specialized equipment and maintenance requirements.
- Slower processing speeds, making it less suitable for high-volume industrial cutting.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- 의료 기기, ~와 같은 stent fabrication and eye surgery (LASIK).
- 마이크로 전자 공학, 포함 precision cutting of silicon wafers and microchips.
- High-end optics, ~와 같은 optical lenses and laser components.
4. Laser Cutting Processes & 기법
Laser cutting is a versatile and precise material processing method that relies on a focused laser beam to cut, 새기다, or mark various materials.
This section provides an in-depth analysis of the main laser cutting processes,
including fusion cutting, flame cutting, sublimation cutting, and remote cutting, as well as essential techniques that enhance efficiency and precision.
4.1 Key Laser Cutting Processes
퓨전 절단 (Melt and Blow Cutting)
Fusion cutting, 도 알려져 있습니다 melt and blow cutting, is a process where a laser melts the material, and a high-pressure inert gas (such as nitrogen or argon) blows away the molten metal.
Unlike flame cutting, fusion cutting does not involve oxidation, 적합하게 만듭니다 high-precision cutting of metals with minimal heat-affected zones (위험요소).
작동 방식
- The laser beam heats the material to its melting point.
- an inert gas jet (usually nitrogen or argon) removes the molten material from the kerf (cutting path).
- 과정 prevents oxidation, resulting in clean and smooth edges.
장점
- 생산합니다 oxidation-free 가장자리, 후 처리의 필요성을 줄입니다.
- 이상적입니다 고정밀 애플리케이션 ~에 스테인레스 스틸, 알류미늄, 그리고 티타늄.
- Enables high-speed cutting with minimal thermal distortion.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- Aerospace and automotive industries for precise metal cutting.
- Medical equipment manufacturing requiring high-quality, contamination-free cuts.
- Precision engineering and electronics, where oxidation-free parts are essential.
불꽃 절단 (Reactive Cutting or Oxygen Cutting)
Flame cutting, 도 알려져 있습니다 oxygen-assisted laser cutting, is a process where a laser heats the material to its ignition temperature, and oxygen reacts with the metal to generate additional heat.
This exothermic reaction helps accelerate the cutting process, making flame cutting suitable for thick materials.
작동 방식
- The laser heats the material to its oxidation temperature.
- A jet of 산소 is introduced, triggering a combustion reaction.
- The reaction produces additional heat, accelerating material removal.
장점
- Efficient for cutting thicker metals (~ 위에 10 mm).
- 용도 lower laser power, making it more cost-effective for heavy industrial applications.
- Enhances cutting speed for carbon steels and low-alloy steels.
제한
- 생산합니다 산화 된 가장자리, requiring post-processing for some applications.
- Less suitable for stainless steel and aluminum due to oxidation resistance.
- Greater heat-affected zones (위험요소), potentially altering material properties.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- Shipbuilding and heavy machinery manufacturing for cutting thick steel plates.
- Structural fabrication for construction and infrastructure projects.
- Automotive and railway industries where large, strong components are required.
승화 절단 (Vaporization Cutting)
개요
Sublimation cutting, 또한 vaporization cutting, is a high-energy process in which a laser heats the material to its boiling point, causing it to transition directly from a solid to a gas.
Unlike fusion and flame cutting, sublimation cutting does not involve molten metal, 이상적입니다 delicate materials and ultra-precise applications.
작동 방식
- The laser beam rapidly heats the material to its vaporization temperature.
- The material transitions directly from solid to gas, without melting.
- Assist gases such as argon or helium help remove vaporized material.
장점
- No molten metal residue, reducing contamination.
- 생산합니다 ultra-precise and smooth cuts, 이상적입니다 thin films and delicate materials.
- Eliminates 열 응력, preserving material properties.
제한
- 필요합니다 high laser power, increasing operational costs.
- Slower cutting speeds compared to fusion and flame cutting.
- 제한 thin materials due to energy-intensive nature.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- Electronics manufacturing, such as cutting silicon wafers and micro-components.
- Medical industry for precise cutting of 생체 의학 임플란트.
- High-end optics and glass cutting for ultra-precise applications.
Remote Laser Cutting
Remote laser cutting is a non-contact cutting process where a high-power laser scans the material without requiring assist gases.
This method enables 빠른, 정밀한, and distortion-free cutting, particularly in high-speed production environments.
작동 방식
- 에이 high-energy laser beam is directed at the material without any physical contact.
- 재료 instantly vaporizes, creating a fine cutting line.
- CNC or robotic systems control the laser’s movement for high precision.
장점
- Eliminates the need for assist gases, reducing operational costs.
- Ultra-fast cutting speeds, 대량 생산에 이상적입니다.
- Minimal mechanical wear, leading to lower maintenance.
일반적인 응용 프로그램
- Automotive industry, 특히 high-speed cutting of thin sheets.
- Textile industry for non-contact fabric cutting.
- Packaging and labeling for intricate laser etching and marking.
4.2 Advanced Laser Cutting Techniques
High-Speed Galvo-Based Laser Cutting
A technique that uses galvanometer-controlled mirrors to rapidly deflect the laser beam, enabling ultra-fast engraving and cutting of thin materials.
일반적인 용도:
- Laser marking and engraving on 금속, 유리, and plastic.
- Micro-cutting in electronics and semiconductor industries.
Hybrid Laser Cutting (Laser & Water Jet Combination)
결합 laser precision 와 water jet cooling system to minimize heat-affected zones, enabling precise cutting of heat-sensitive materials.
일반적인 용도:
- 절단 composite materials and heat-sensitive plastics.
- Aerospace industry for high-strength lightweight components.
Multi-Axis Laser Cutting (5-Axis & 6-Axis Systems)
Unlike conventional 2D laser cutters, multi-axis systems can cut in three dimensions, enabling the fabrication of complex geometries.
일반적인 용도:
- Aerospace and automotive industries ~을 위한 curved and angled cuts.
- 고급의 robotic laser cutting in automation.
5. Materials Used in Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology is highly versatile and can process a wide range of materials, 포함 궤조, 플라스틱, 도예, 복합재, and even organic materials like wood and textiles.
5.1 Metals for Laser Cutting
Metals are among the most commonly processed materials in laser cutting due to their widespread use in manufacturing, 건설, and engineering.
Different types of metals require different laser power levels, assist gases, and cutting techniques to achieve precise and high-quality results.
강철 (온화한 강철, 탄소강, and Stainless Steel)
온화한 강철 & 탄소강
- 형질: 탄소강 contains varying amounts of carbon, which influences its hardness and strength.
- Cutting Considerations: 필요합니다 oxygen-assisted laser cutting to enhance cutting speed through an exothermic reaction.
- 응용: 구조 구성 요소, 자동차 부품, 산업 기계, 중장비 제조.
스테인레스 스틸
- 형질: 부식성, 고강도, and excellent durability.
- Cutting Considerations: Best processed using nitrogen-assisted fusion cutting to achieve oxidation-free, 깨끗한 가장자리.
- 응용: 의료기구, 항공 우주 구성 요소, 식품 가공 장비, 그리고 장식 패널.

알루미늄 및 알루미늄 합금
- 형질: 경량, 부식성, and excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
- Cutting Considerations: 필요합니다 high-power fiber or CO₂ lasers. Nitrogen or argon assist gas prevents oxidation and ensures a clean cut.
- 응용: Aircraft parts, automotive body panels, 소비자 전자 장치, and architectural structures.
티타늄 및 티타늄 합금
- 형질: 고강도, 낮은 무게, and excellent resistance to corrosion and high temperatures.
- Cutting Considerations: Argon or helium assist gases are used to prevent oxidation and contamination. High laser power is required due to titanium’s reflectivity.
- 응용: Aerospace and aviation, 의료 임플란트, and high-performance industrial components.
구리와 황동
- 형질: 높은 열 및 전기 전도도, excellent malleability, 그리고 부식 저항.
- Cutting Considerations: Highly reflective and conductive, 요구 섬유 레이저 ~와 함께 higher power to cut effectively. Nitrogen is used to prevent oxidation.
- 응용: 전기 구성 요소, 배관 설비, 열교환 기, and decorative metalwork.
5.2 Non-Metallic Materials for Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is widely used for non-metal materials, especially in industries requiring 복잡한 디자인, 좋은 세부 사항, and non-contact processing.
Plastics and Polymers
Plastics are extensively used in laser cutting due to their affordability, 가벼운 특성, 처리의 용이성. 하지만, some plastics emit toxic fumes when cut, requiring proper ventilation.

Commonly Used Plastics
- 아크릴 (PMMA): 생산합니다 우아한, flame-smooth edges when cut with a CO₂ laser. Used in signage, display cases, 그리고 장식 패널.
- 폴리카보네이트 (PC): Challenging to cut with lasers due to its tendency to burn; used in industrial equipment and protective shields.
- 폴리에틸렌 (체육) & 폴리 프로필렌 (PP): Used for packaging and lightweight components. Low melting points require controlled laser settings.
- ABS (아크릴로니트릴 부타디엔 스티렌): Used in automotive components and consumer electronics. 하지만, it releases harmful fumes when laser-cut.
Wood and Wood-Based Materials
Laser cutting is widely used in woodworking, furniture manufacturing, and crafts due to its ability to create intricate patterns and fine details.
Commonly Processed Wood Types
- Plywood: 필요합니다 controlled laser settings to prevent charring.
- MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard): Often used in furniture and signage, but produces significant smoke.
- Solid Wood: Cuts well but may require 후 처리 to enhance the finish.
5.3 Composite and Advanced Materials
Composite materials offer unique properties by combining two or more distinct materials.
Laser cutting can be challenging due to varying 녹는 점, 열 팽창, and material compositions.
Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymers (CFRP)
- 형질: 경량, 고강도, used in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Cutting Considerations: 필요합니다 high-power CO₂ or fiber lasers. Thermal damage and delamination are concerns.
- 응용: 항공기 구성 요소, 스포츠 장비, and racing car parts.
Glass and Ceramics
- 형질: Brittle but highly resistant to heat and chemicals.
- Cutting Considerations: Ultra-short pulse lasers (such as femtosecond lasers) are ideal to prevent cracking.
- 응용: 전자 장치, 의료기기, 건축 응용 프로그램.
5.4 Choosing the Right Material for Laser Cutting
Factors to Consider
- 반사율: Metals like 알류미늄 그리고 구리 require specialized 섬유 레이저 due to high reflectivity.
- 열전도율: High thermal conductivity materials like copper and brass need higher power levels to ensure efficient cutting.
- Fume Emission: Some plastics and composite materials produce toxic gases, requiring proper ventilation.
- 에지 품질: Certain materials require assist gases (예를 들어, 질소, 산소, 또는 아르곤) to improve edge finish and prevent oxidation.
| 재료 | Best Laser Type | 일반적인 응용 프로그램 | Assist Gas Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| 온화한 강철 | co₂, Fiber | 자동차, 건설, 산업 부분 | 산소, 질소 |
| 스테인레스 스틸 | Fiber, co₂ | 의료, 항공우주, 주방 용품 | 질소, Argon |
| 알류미늄 | Fiber, co₂ | 항공 우주, 전자 제품, 간판 | 질소 |
| 티탄 | Fiber | 항공 우주, 의료 임플란트 | Argon, Helium |
| 구리 & 놋쇠 | Fiber | 전기 같은, 연관, 장식 | 질소 |
| 아크릴 (PMMA) | co₂ | 간판, displays, 보석류 | 없음 |
| 목재 (Plywood, MDF) | co₂ | 가구, crafts, 건축 요소 | 없음 |
| 탄소 섬유 | Fiber, co₂ | 항공 우주, 자동차, 스포츠 장비 | 없음 |
| 유리 & 도예 | Femtosecond Laser | 전자 장치, 광학, medical applications | 없음 |
6. Key Advantages of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology is especially popular for its precision, 능률, 다재, and ability to handle complex geometries.
Below are the key advantages of laser cutting that have contributed to its widespread adoption in both small-scale and large-scale manufacturing.
높은 정밀도와 정확도
One of the most significant advantages of laser cutting is its exceptional precision and accuracy.
Lasers can achieve extremely tight tolerances, often as fine as 0.1 mm or even smaller, depending on the material and laser type.
This makes it ideal for industries where 고품질, 뒤얽힌, and detailed cuts 필요합니다, 예를 들어 in 항공 우주 구성 요소, 의료기기, and microelectronics.
Key Points
- Minimal kerf width: The laser’s focused beam minimizes the width of the cut, leading to more accurate, consistent results.
- No tooling wear: Unlike traditional cutting methods that wear out tools over time, lasers maintain precision throughout the process.
- 복잡한 기하학: Lasers can easily cut shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with mechanical tools.
재료 전반의 다양성
Laser cutting can process a wide range of materials, 금속을 포함하여, 플라스틱, 도예, 유리, 복합재, and even organic materials like wood and textiles.
This versatility makes it highly adaptable across industries.
The laser’s ability to cut or engrave a variety of materials without needing extensive retooling means businesses can efficiently switch between different materials as needed.
Key Points
- Wide range of materials: Laser cutting can handle materials from thin sheets to thicker plates.
- 맞춤화: Laser systems can be used to cut, 새기다, and etch with a high degree of customization on nearly any material.
- 재료 폐기물 감소: The precision of laser cutting minimizes scrap, 허용 optimal material usage.
Clean Cuts and Smooth Edges
Laser cutting produces 매끄러운, 깨끗한 가장자리 that often require little to no post-processing.
This is because the laser’s intense heat melts the material and then cools it almost instantaneously, leaving behind a smooth, polished edge.
This feature is particularly beneficial when working with thin or delicate materials, where traditional cutting methods might cause distortion or a rough finish.
Key Points
- No burrs or rough edges: Laser cutting eliminates the need for secondary operations like deburring or edge finishing.
- Less distortion: Since the laser cuts with minimal contact and heat input, the material is less likely to warp or distort.
- Fine details: The laser can achieve intricate cuts, making it ideal for designs requiring precise detailing, such as jewelry, 간판, or electronic components.
속도와 효율성
Laser cutting is a highly efficient process, 헌금 rapid cutting speeds, 특히 thin materials.
그만큼 non-contact nature of the laser means there is no physical wear and tear on tools, enabling faster turnaround times without compromising quality.
The technology also offers the ability to automate the cutting process, increasing productivity and reducing labor costs in the long term.
Key Points
- High cutting speed: Lasers are able to cut much faster than traditional methods, especially for materials that are difficult to machine.
- No tool changes required: Laser cutting can quickly switch between different materials or designs without the need to change tools.
- Automation capabilities: Laser systems can be integrated into fully automated production lines, further improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Ability to Cut Complex Shapes
Laser cutting excels in creating 복잡한 기하학 and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional cutting methods.
Whether cutting 날카로운 각도, 곡선, or internal holes, lasers can handle highly detailed designs with ease.
This flexibility in design is crucial for industries that require 관습, one-of-a-kind parts 또는 소량 생산 실행.

Key Points
- Tight radii: The laser’s narrow beam enables it to cut very tight corners and intricate shapes.
- No tooling limitations: Traditional cutting tools can be limited by the shape or geometry of the tool itself.
With lasers, virtually any shape can be cut directly from a digital design without worrying about tool geometry. - Adaptability: Laser cutting allows for design changes with minimal impact on the production process.
Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (위험요소)
Compared to traditional cutting techniques, laser cutting creates a relatively small heat-affected zone (위험요소).
The HAZ refers to the portion of the material that experiences heat exposure, which could affect its properties, 경도와 힘과 같은.
Because the laser beam is highly focused and precise, it only heats a very small area, leaving the surrounding material largely unaffected.
Key Points
- Reduced material distortion: With less heat applied, there’s a lower risk of warping or shrinking in the material.
- Ideal for heat-sensitive materials: Materials that are prone to thermal damage, ~와 같은 plastics and thin metals, benefit from laser cutting’s low heat input.
- 구조적 무결성 향상: The minimal heat exposure helps preserve the material’s 물리적 특성 for high-strength applications.
High Degree of Automation and Precision
Laser cutting machines can be integrated into automated production lines, 허용 마디 없는, high-precision cutting.
With the integration of 컴퓨터 보조 디자인 (치사한 사람) 그리고 컴퓨터 보조 제조 (캠), laser cutting systems can operate autonomously with minimal human intervention.
This level of automation reduces errors, improves consistency, and enhances overall production efficiency.
Key Points
- Seamless integration: Laser cutting can be easily integrated into 자동화 된 시스템, including robotic arms and conveyor belts, to achieve fully automated production lines.
- Consistent quality: Laser cutting ensures 일관된, 반복 가능한 결과, even in large production volumes.
- Quick changeovers: Automated systems allow for rapid reprogramming of the laser cutter for different jobs, improving flexibility in production.
7. 제한 & Challenges of Laser Cutting
While laser cutting offers significant advantages, it does come with certain limitations and challenges.
아래에, we highlight the key factors businesses must consider when using laser cutting technology.
재료 제한
Laser cutting works well with many materials, but thick or highly reflective materials like 구리 그리고 놋쇠 can present difficulties.
Materials such as 알류미늄 also cause laser energy reflection, reducing cutting efficiency. Some materials like 도예 are not suitable for laser cutting at all.
높은 초기 투자
The cost of purchasing laser cutting machines, especially industrial-grade systems, is high.
In addition to the initial investment, maintenance and energy costs can also add to the total cost of ownership, making it challenging for smaller businesses to afford.
Limited Thickness for Certain Materials
Laser cutting is most efficient with thin to medium-thickness materials.
Cutting thicker materials, especially metals, can reduce quality, requiring more passes and potentially leading to heat distortion or slower cutting speeds.
후 처리 요구 사항
Though laser cutting produces precise cuts, materials often require 디버링 그리고 세련 post-processing to remove rough edges or slag, adding extra time and cost to the process.
Cutting Speed for Certain Applications
For thicker or reflective materials, laser cutting speeds can slow down. This may not be an issue for smaller runs but can be a bottleneck in mass production, impacting overall efficiency.
환경 문제
Laser cutting can generate harmful fumes and gases, especially when cutting plastics or coated metals. Proper ventilation and filtering systems are required to mitigate environmental impact.
Skill Requirements and Training
Operating laser cutting machines requires specialized training for proper machine configuration, 자재 취급, 그리고 안전.
Lack of skilled operators can compromise the process, reducing efficiency and quality.
8. Applications of Laser Cutting Across Industries
조작 & Industrial Fabrication
Laser cutting is widely used for sheet metal 처리, custom parts fabrication, and industrial machinery production.
It enables manufacturers to achieve complex geometries with high precision, reducing the need for secondary processing.
자동차 & 항공 우주
에서 자동차 산업, laser cutting is used for precision welding, body panel fabrication, and engine component manufacturing.
항공 우주에서, it allows for lightweight structural components with tight tolerances, 연비 개선.
의료 & 의료
레이저 절단은 복잡한 생산을 가능하게합니다 의료기기, such as stents, 수술기구, and prosthetic components.
Femtosecond lasers are particularly useful for cutting biocompatible materials without causing heat damage.
전자 장치 & 반도체 산업
전자 장치에서, laser cutting is used for printed circuit boards (PCB), microchips, and high-precision 전자 인클로저.
The ability to cut with sub-micron accuracy makes it invaluable in semiconductor manufacturing.
9. Laser Cutting vs. Water Jet Cutting vs. Plasma Cutting vs. 기계적 절단: 주요 차이점
| 특징 | 레이저 절단 | Water Jet Cutting | 플라즈마 절단 | 기계적 절단 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 정도 | ±0.1mm or better | ±0.25mm to ±0.5mm | ±1mm to ±2mm | ±0.2mm to ±1mm |
| 열 영향 구역 (위험요소) | 최소 | 없음 | 더 큰 | 더 큰 |
| 재료 | 얇은 금속, 플라스틱, 목재 | 두꺼운 재료 (stone, 유리) | Thick metals (강철, 알류미늄) | Thick metals, particularly steel and aluminum |
| 절단 속도 | 얇은 재료의 경우 빠릅니다 | Slower than laser cutting | Fast for thick metals | Slower for intricate designs, faster for basic cuts |
| 비용 | 높은 장비 비용, but efficient for high precision | High initial setup cost but low running costs | Lower initial cost, but rougher cuts | Lower initial investment, more labor-intensive |
| 도구 마모 | No tool wear | No tool wear | Some wear on electrodes | Significant wear on tools (톱, 훈련) |
| 후 처리 | 최소 | No HAZ, but may need polishing | Rough edges that need cleanup | Often needs deburring or smoothing |
10. Innovations and Future Trends in Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology has undergone significant advancements in recent years, driven by innovations that enhance speed, 정도, and material compatibility.
As the demand for efficiency and versatility continues to grow across industries, laser cutting is poised for further transformation.
여기, we explore some of the most promising innovations and future trends in laser cutting.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (일체 포함) and Machine Learning
인공 지능 (일체 포함) 그리고 기계 학습 are increasingly being incorporated into laser cutting systems to improve performance and reduce errors.
AI algorithms can analyze cutting patterns, optimize path planning, and adjust parameters in real-time to adapt to changes in material properties or thickness.
This level of automation reduces the need for manual intervention and enhances the precision of the cutting process.
주요 이점:
- Real-time adaptation: AI can continuously monitor cutting conditions, such as material surface variations, to adjust parameters in real-time for optimal results.
- Increased efficiency: Machine learning algorithms can predict potential failures or issues based on historical data, enabling preventive measures to be taken before they cause downtime.
- Improved material utilization: AI can optimize cutting paths, reducing material waste and maximizing the output from a given sheet or piece.
Fiber Lasers and Advancements in Laser Source Technology
Fiber lasers have already surpassed traditional CO2 lasers in many applications due to their higher efficiency, faster cutting speeds, and ability to work with a broader range of materials.
Laser technology continues to evolve, with innovations in beam quality, 힘, and wavelength, enabling faster cutting of thicker materials with improved edge quality.
미래의 트렌드:
- High-power fiber lasers: Advances in high-power fiber lasers are allowing for cutting thicker materials, especially metals like 스테인레스 스틸, 알류미늄, 그리고 티탄.
This reduces the need for additional equipment like plasma or mechanical cutting for heavy-duty applications. - Laser beam quality: Higher beam quality from advanced fiber lasers results in finer cuts and better surface finishes, which can be critical for industries like aerospace and medical devices.
- Cost reductions: As fiber laser technology becomes more affordable,
it is expected to be more accessible to a broader range of manufacturers, including small and medium-sized enterprises (중소기업).
Hybrid Laser Cutting and 3D Printing
의 조합 레이저 절단 그리고 3D 인쇄 technologies is an exciting area of innovation. Hybrid systems are emerging that integrate laser cutting with 첨가제 제조 프로세스.
This allows manufacturers to combine the precision and material efficiency of laser cutting with the flexibility of 3D printing to produce complex parts and components.
주요 이점:
- Enhanced design possibilities: Hybrid systems offer greater design flexibility, enabling the production of complex geometries that cannot be achieved with traditional cutting methods alone.
- Faster prototyping: Manufacturers can produce prototypes faster by combining additive and subtractive processes, reducing time-to-market for new products.
- 재료 효율성: Hybrid systems allow for more efficient use of materials by adding layers of material through 3D printing and finishing them with laser cutting, resulting in less waste.
Automation and Robotics in Laser Cutting
통합 로봇공학 with laser cutting systems is accelerating.
Automated laser cutting cells are becoming more common, enabling continuous, high-speed operations with minimal human intervention.
Robotics in laser cutting helps improve precision, streamline material handling, and reduce operational costs.
주요 이점:
- Increased throughput: Robotics systems enable faster material loading and unloading, reducing downtime and increasing production capacity.
- Precision and flexibility: Robots can adapt to various tasks, including part picking, 포지셔닝, and cutting, with high precision and flexibility for complex or customized components.
- 24/7 작업: Automated systems can operate around the clock, leading to higher production efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Sustainable Laser Cutting
As sustainability becomes a top priority for industries, laser cutting technology is adapting to meet eco-friendly manufacturing standards.
Several innovations are making laser cutting more energy-efficient and reducing its environmental impact.
지속 가능한 관행:
- Laser cutting with recyclable materials: There is an increasing focus on using recycled metals and other eco-friendly materials in laser cutting processes.
Manufacturers are also improving the recycling of laser-cut scrap materials, contributing to waste reduction. - Energy-efficient lasers: New laser technologies, 특히 섬유 레이저, are more energy-efficient than traditional CO2 lasers, reducing power consumption during cutting operations.
- 폐기물 감소: The high precision of laser cutting results in less material waste compared to traditional cutting methods, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
산업과의 통합 4.0 그리고 스마트 제조
Laser cutting technology is also evolving as part of the broader trend toward 산업 4.0 그리고 스마트 제조.
The integration of laser cutting systems with IoT (사물의 인터넷), cloud computing, 그리고 big data allows for smarter, more connected production environments.
주요 이점:
- Predictive maintenance: IoT-enabled sensors monitor the performance of laser cutting machines in real time,
detecting issues such as wear and tear or misalignment before they lead to equipment failure. - Data-driven optimization: Cloud-based platforms can collect and analyze data from laser cutting machines, enabling manufacturers to optimize processes, 다운 타임을 줄입니다, 품질을 향상시킵니다.
- Remote monitoring and control: Manufacturers can monitor and adjust laser cutting systems remotely, offering greater flexibility and reducing the need for on-site interventions.
11. 결론
Laser cutting continues to push the boundaries of modern manufacturing, 비교할 수 없는 정밀도 제공, 속도, 그리고 다양성.
기술이 발전함에 따라, industries adopting AI-driven optimization, sustainable practices, and hybrid manufacturing will gain a competitive edge.
Investing in laser cutting technology today will drive innovation and efficiency in the years to come.
랑헤 is the perfect choice for your manufacturing needs if you need high-quality Laser cutting services.