How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting operates by directing a high-powered laser beam onto a material to cut, engrave, or etch precise designs. The process involves several key steps and components, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in every application. Here’s how it works:
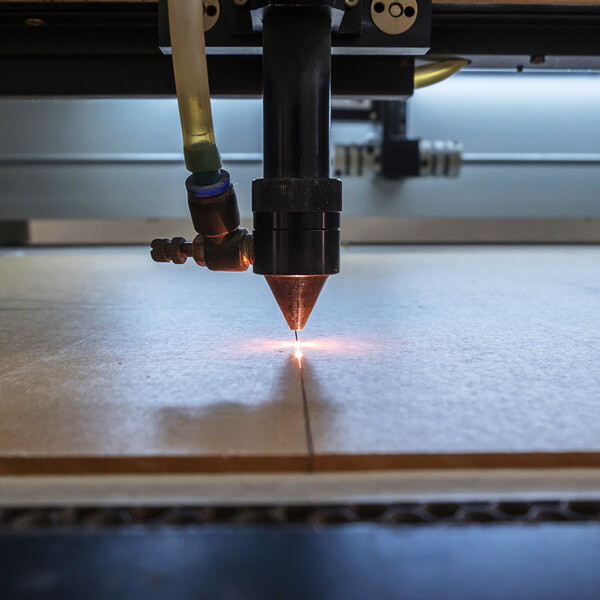
Laser Beam Generation
A laser source generates a concentrated beam of light, which is then directed through lenses or mirrors to focus on the material's surface.
Cutting Process
The laser beam's high intensity heats and vaporizes the material, creating a fine kerf (cut width) that follows the pre-programmed design.
Material Ejection
Gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or compressed air may be used to blow away melted or vaporized material, leaving clean, precise edges.
Computer Control
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems guide the laser beam for highly accurate and repeatable results.
Finishing the Cut
The process results in clean, precise edges with minimal to no post-processing required. Modern laser cutting technology ensures smooth finishes and tight tolerances, making it suitable for both functional and aesthetic applications.


















