1. Zavedení
Zátkový ventil je všestranný čtvrtotáčkový ventil široce používaný pro izolaci, odklon, a občasné škrcení v průmyslových systémech.
Jeho jednoduchá konstrukce – válcová nebo kuželová kuželka rotující v těle ventilu – nabízí rychlý provoz, pokles nízkého tlaku, a robustní spolehlivost.
Pochopení jeho principů, materiály, Metriky výkonu, a průmyslové aplikace je zásadní pro výběr správného ventilu pro vysoký tlak, Abrasive, nebo prostorově omezené služby.
2. Co je to zástrčka?
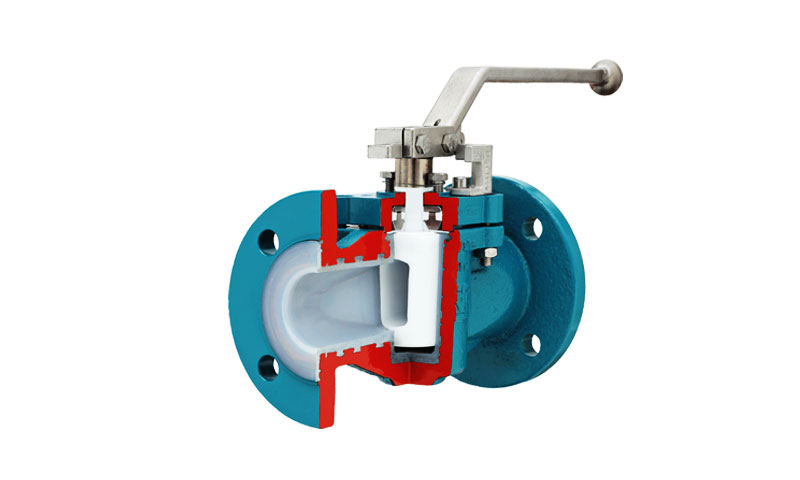
A zátkový ventil je specializovaný čtvrtotáčkový rotační ventil široce používaný v průmyslových potrubních systémech pro izolaci průtoku, odklon, a občasné škrcení.
Základní princip fungování spoléhá na a válcová nebo kuželová zátka uloženy v těle ventilu, který se otáčí, aby buď vyrovnal svůj vnitřní port s potrubím pro neomezený průtok, nebo aby úplně zablokoval průchod.
Tento jednoduchý, ale robustní mechanismus umožňuje rychlý provoz v úhlu 90°, nabízí efektivitu i spolehlivost v kritických aplikacích.
Základní vlastnosti
- Čtvrtotáčkový provoz
Rychlá aktivace (typicky 90°) — ideální pro nouzovou izolaci, úkoly a aplikace přepínačů, kde je vyžadována rychlá akce zapnutí/vypnutí. - Jednoduchý, Cesta toku s nízkou překážkou
Konfigurace s plným portem poskytují prakticky průtok potrubím s minimálním poklesem tlaku; Možnosti redukovaného portu vyměňují kapacitu průtoku za nižší točivý moment a náklady. - Konfigurace více portů
Dva-, tři- a čtyřcestné uspořádání zástrček umožňuje odklon, Míchání, vzorkování a složité směrování bez více ventilů. - Všestrannost těsnění
K dispozici s kov na kov sedadla pro vysokoteplotní/abrazivní práce, pružný (PTFE/RPTFE, Elastomery) sedadla pro bublinotěsné uzavření a nízký točivý moment, nebo namazaný systémy, které prodlužují životnost sedadla ve špinavých nebo erozivních médiích.
3. Klasifikace zátkových ventilů podle konstrukce
Kuželové ventily jsou kategorizovány na základě Mechanický design, Metoda těsnění, a konfiguraci průtoku.
Pochopení těchto klasifikací pomáhá technikům vybrat správný ventil pro tlak, teplota, tok, a požadavky na služby.

Na základě typu zástrčky
| Typ | Popis | Výhody | Typické aplikace |
| Válcový zátkový ventil | Přímá válcová zátka se otáčí uvnitř odpovídající tělesné dutiny; nejjednodušší design. | Kompaktní, nákladově efektivní, pokles nízkého tlaku. | Voda, plyn, nízkotlaké chemické linky. |
| Kónicky (Zúžené) Zástrčný ventil | Kónická zátka zaklíněná do těla pro těsnější utěsnění. | Vynikající těsnění; zvládá vyšší tlak a teplotu. | Petrochemický, olej & plyn, parní linky. |
Na základě konfigurace portu
| Typ portu | Popis | Výhody | Typické aplikace |
| Přes Port (Plný přístav) | Port odpovídá průměru potrubí; průtoková cesta přímo skrz. | Minimální pokles tlaku; vysoká průtoková kapacita. | Hromadná přeprava tekutin, potrubí, manipulace s kejdou. |
| Snížený port | Port menší než otvor trubky. | Nižší provozní moment; nákladově efektivní. | Systémy se středním průtokem, přístrojové řady. |
| Multi-Port (Tři- nebo Čtyřcestný) | Umožňuje odklon toku, Míchání, nebo vzorkování přes více portů. | Nahrazuje více ventilů; flexibilní směrování. | Odběr vzorků, odkláněcí povinnosti, chemické reaktory. |
Na základě Plug Support
| Typ podpory | Popis | Výhody | Omezení |
| Plovoucí zástrčka | Zástrčka leží mezi sedadly a volně se otáčí. | Samovyrovnávací; jednoduchá konstrukce. | Vyšší točivý moment u velkých rozměrů; omezené použití vysokého tlaku. |
| Zástrčka na čepu | Hmoždinka ukotvená horním a/nebo spodním ložiskem. | Snižuje provozní točivý moment; stabilní ve vysokotlakých nebo velkorozměrových aplikacích. | Složitější design; Vyšší výrobní náklady. |
Založeno na designu těsnění
Prodloužená životnost sedadla; hladký provoz ve znečištěných nebo erozivních kapalinách.
Pravidelná údržba; není ideální pro sanitární aplikace.
lymerská sedadla zajišťují těsné utěsnění.
| Typ těsnění | Popis | Výhody | Omezení |
| Metal-to-Metal | Pevné sedadlo se přímo dotýká zástrčky. | Vysoká teplota, vysoký tlak, abrazivní servis. | Vyžaduje vyšší točivý moment; možnost zadření bez mazání. |
| Odolná sedadla (PTFE, Rptfe)
</td> |
Elastomer nebo po | Nízký točivý moment; bublinotěsné uzavření; chemická odolnost. | Omezený teplotní rozsah; potenciální degradace agresivními médii. |
| Lubr |
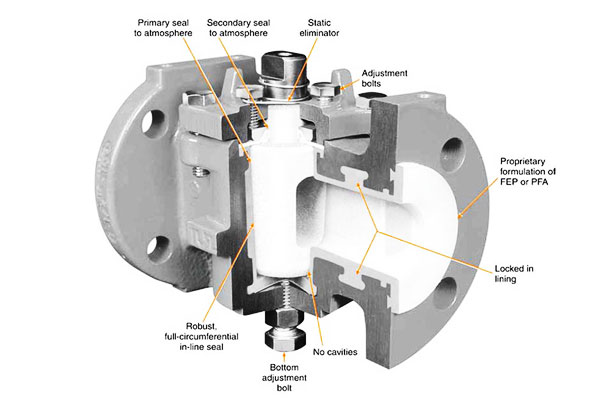
4. Hlavní součásti a materiály zátkového ventilu
Výkon kuželkového ventilu, trvanlivost, a vhodnost pro konkrétní aplikace závisí na něm komponenty a materiály.
Každá část je navržena tak, aby vydržela tlak, teplota, koroze, a eroze při zajištění hladkého provozu a nepropustného těsnění.

Hlavní komponenty
| Komponent | Popis | Funkce |
| Tělo ventilu | Vnější kryt, který obsahuje zástrčku a porty. | Podporuje tlakové zatížení, poskytuje cestu toku, a připojuje se k potrubí. |
| Zástrčka | Válcový nebo kuželový rotační prvek s jedním nebo více porty. | Řídí tok zarovnáním nebo blokováním portu(s); primární prvek řízení průtoku. |
| Sedadla | Kovové nebo pružné povrchy, proti kterým zátka těsní. | Zajišťuje bublinotěsné uzavření a zachovává dlouhodobou integritu těsnění. |
| Zastavit / Zacházet s | Hřídel nebo páka sloužící k otáčení zástrčky. | Přenáší točivý moment z ručního nebo automatického pohonu na zástrčku. |
| Komora maziva (volitelný) | Nádržka mezi zátkou a tělem naplněná mazivem (pro mazané kuželkové ventily). | Snižuje tření, prodlužuje životnost sedačky, a zabraňuje zadření nebo korozi. |
| Ložiska / čepy (pro čepové zástrčky) | Podpěry v horní a/nebo spodní části zástrčky. | Snižuje provozní moment a stabilizuje kuželku ve velkých nebo vysokotlakých ventilech. |
| Žláza / Balení | Těsnící prvek kolem dříku nebo rozhraní rukojeti. | Zabraňuje prosakování podél představce/držadla; umožňuje plynulé otáčení. |
Výběr materiálů
| Komponent | Typické materiály | Klíčové vlastnosti |
| Tělo & Bonnet | Uhlíková ocel (A216 WCB), Nerez (304, 316), Duplex, Slitina 20, Slitiny niklu | Pevnost, odolnost proti korozi, tolerance teploty |
| Zástrčka | Stejné jako tělo nebo tvrdé (Stellite, Překrytí WC) | Nosit odpor, rozměrová stabilita, Chemická kompatibilita |
| Sedadla | Kov (Stellite, Monel), PTFE/RPTFE, UHMWPE | Těsnost těsnění, chemická odolnost, Nízké tření |
| Zastavit / Zacházet s | Nerez, Slitinová ocel | Pevnost, torzní tuhost, odolnost proti korozi |
| Lubrikant | Minerální olej, syntetické mazivo, nebo lubrikanty schválené FDA | Snižuje tření a chrání před korozí v mazaných ventilech |
5. Průtokové charakteristiky a hydraulické chování

Schopnost průtoku (CV) — typické rozsahy
- Malé kuželkové ventily velikosti nástroje (¼ – 1) může mít Cv ~ 0,1–5.
- Běžné velikosti procesu (2–6) typicky rozsah Cv ~ 5–200 v závislosti na designu portu (plný port vs. snížený port).
- Kuželové ventily velkého průměru (8+) může dosáhnout velmi vysokých hodnot Cv, srovnatelné s kulovými ventily a často převyšující kulové ventily pro stejnou velikost.
Pokles tlaku a škrcení
- Kuželové ventily jsou primárně určeny pro zapnuto/vypnuto nebo převaděč servis.
Zatímco mohou být použity pro škrcení, jsou méně ideální než kulové ventily pro přesnou modulaci z důvodu potenciální nelineární charakteristiky proudění a opotřebení sedla při škrcení pod vysokým ΔP. - Pokles tlaku se zvyšuje s průtokem a snižuje se s velikostí portu; služba s vysokým ΔP vyžaduje speciální úpravy (vícestupňové nebo tlak snižující zátky) aby se zabránilo hluku a erozi.
6. Metriky výkonu a třídy
| Metrický | Typická starost / rozsah |
| Tlaková třída | ANSI 150–2500 běžné; vyšší s kovanými vzory |
| Teplotní rozsah | Kryogenní (s vhodnými materiály) až ≈400–600°C v běžných slitinách; speciální slitiny rozšiřují sortiment |
| Únik | Kovová sedadla: nízký únik, ale ne ve všech případech vzduchotěsné; pružná sedadla: bublinková (prakticky nulový únik) |
| Životnost cyklu | Mazaná kovová sedadla: dlouhá životnost v čistém provozu; pružná sedadla: tisíce až desetitisíce cyklů |
| Fugitivní emise | Zmírnit pomocí měchů, živé balení, a vyhovující těsnění vřetene |
| Normy & testy | Zkouška tlaku skořepiny/sedadla, testování těsnosti sedadla, NDT na kritických částech (radiografie, MPI) |
7. Výrobní proces zátkového ventilu
Výroba kuželkových ventilů zahrnuje precizní zpracování obsazení, obrábění, shromáždění, a testování aby byla zajištěna trvanlivost, nepropustné těsnění, a spolehlivý provoz v různých průmyslových podmínkách.

Odlévání nebo kování těla a zástrčky
Ventil tělo a zástrčku tvoří konstrukční jádro kuželkového ventilu. Mohou být vyrobeny prostřednictvím:
- Lití písku: Společné pro střední- na velkorozměrové ventily. Poskytuje flexibilitu ve složitých geometriích, včetně víceportových těles, a umožňuje vestavěné funkce, jako je podpora čepů.
Tepelné zpracování po lití snižuje zbytkové pnutí. - Investiční lití (Ztracený vosk): Nabízí výjimečnou rozměrovou přesnost a hladké povrchy, ideální pro přesné nebo menší ventily s úzkými tolerancemi.
- Kování: Produkuje husté, vysokopevnostní komponenty pro vysokotlaké nebo kritické aplikace. Kované ventily mají méně dutin a vynikající odolnost proti únavě, vhodné pro potrubní standardy API 6D.
Přesné obrábění
Po lití nebo kování, Komponenty podléhají CNC a ruční obrábění pro dosažení přesných tolerancí a hladkých povrchových úprav:
- Vrtání a broušení zástrček: Zajišťuje, že se zátka volně otáčí a zároveň udržuje těsné utěsnění vůči sedlu.
- Obrábění sedadla: Kovová nebo pružná sedla jsou obrobena s tolerancí na úrovni mikronů, aby bylo zajištěno těsné uzavření.
- Zarovnání portů: Rozhodující pro vícecestné ventily pro zajištění správných průtokových cest a minimalizaci poklesu tlaku.
- Povrchová úprava: Lapování, leštění, nebo honování snižuje tření, zabraňuje zadření, a zlepšuje dlouhodobou spolehlivost těsnění.
Navařování a povlaky
Pro zvýšení trvanlivosti v Abrasive, erozivní, nebo korozivní média, zástrčky a sedla mohou být:
- Hardfaced s Stellite, Karbid wolframu, nebo slitiny na bázi niklu, zvýšení odolnosti proti opotřebení a prodloužení životnosti.
- Potažené s vrstvami odolnými proti korozi, jako je PTFE, Položení niklu, nebo epoxid.
- Mazaný ve specializovaných ventilech pro udržení provozu s nízkým točivým momentem, zabránit zadření, a prodloužit životnost těsnění, zejména při vysokotlakých suspenzních aplikacích.
Montáž a montáž
Montáž je přesná operace, která zajišťuje správné provedení zarovnání, plynulé ovládání, a celistvost těsnění:
- Vložení zástrčky: Pečlivě umístěn v těle; v případě potřeby namažte.
- Instalace představce a čepu: Ložiska a podpěry čepu jsou namontovány pro snížení provozního točivého momentu a stabilizaci velkých kuželek pod vysokým tlakem.
- Seřízení ucpávky a ucpávky: Zabraňuje úniku podél představce a zároveň zajišťuje plynulou rotaci.
- Ověření těsnění a sedla: Kovová nebo pružná sedla jsou kontrolována na správné stlačení, zarovnání, a povrchový kontakt.
Testování a kontrola kvality
Každý kuželkový ventil prochází přísným testováním API, ISO, a normy ASTM:
- Hydrostatické a pneumatické tlakové zkoušky: Ověřte integritu těla a sedadla při jmenovitých pracovních tlacích a maximálních přípustných tlacích.
- Testy těsnosti sedadel: Potvrďte bublinotěsné uzavření podle ISO 5208 nebo API 598.
- Rozměrové ověření: CNC souřadnicové měřicí stroje (Cmm) zajistit shodu s konstrukčními specifikacemi.
- Provozní měření točivého momentu: Zajišťuje plynulé otáčení bez nadměrné síly, kritické pro automatické nebo dálkově ovládané ventily.
- Nedestruktivní testování (Ndt): Techniky, jako je penetrant barviv, magnetická částice, nebo ultrazvukové testování odhalí mikrotrhliny, pórovitost, nebo vady odlitku.
8. Výhody a omezení

Klíčové výhody zátkového ventilu
- Odolnost proti abrazivním kapalinám: Excentrické zátky se sedlem z karbidu wolframu trvají 300% delší než kulové ventily v důlních kalech (podle časopisu Mining Engineering Journal).
- Nízký pokles tlaku: Plně otevřené kuželové ventily snižují spotřebu energie čerpadla o 10–15 % vs. Globe ventily (Údaje EPA Energy Star).
- Rychlý provoz: Čtvrtotáčkové provedení (0.5–2s pro automatické ventily) – kritické pro nouzové odstavení (NAPŘ., výrony ropných vrtů).
- Všestrannost: Zvládá tekutiny, plyny, a kaly v rozmezí -196 °C až 815 °C – jeden typ ventilu pro více procesních proudů.
- Únik těsný výkon: Ventily s měkkým sedlem dosahují netěsnosti třídy VI (≤0,00001 %) – zabraňuje ztrátě drahých/toxických kapalin.
Omezení Plug Valve
- Požadavky na vysoký točivý moment: Nemazané ventily s kovovým sedlem potřebují 2–3x větší krouticí moment než kulové ventily – větší ventily vyžadují nákladné pneumatické/hydraulické pohony.
- Potřeby údržby: Mazané ventily vyžadují čtvrtletní vstřikování maziva – nedostatečná údržba způsobuje zablokování kuželky (prostoje 4–8 hodin na incident).
- Limity vysokých teplot: Měkká sedadla (PTFE) degradovat nad 260°C – omezeno na provoz při nízkých teplotách (NAPŘ., Zpracování potravin).
- Náklady: Excentrické a vysoce výkonné kuželkové ventily stojí o 20–50 % více než kulové ventily – opodstatněné pouze pro drsné podmínky.
- Kaše s velkými pevnými látkami: Víceportové a válcové zátky se ucpávají pevnými částicemi >5 mm – vyžadují sítka nebo excentrická provedení.
9. Aplikace zátkového ventilu
Kuželové ventily vynikají v náročných průmyslových prostředích, kde jiné ventily selhávají.

Níže jsou uvedeny klíčové sektory a případy použití:
Olej & Plyn
- Proti proudu (Studny): Kuželové ventily mazané API 6A (1000 bar, 350° C.) regulovat ropu a kyselý plyn – soulad s NACE MR0175 odolává korozi H₂S.
- Střední proud (Potrubí): Excentrické kuželové ventily (6d oheň) fungují jako blokové ventily pro zemní plyn (průtoky až 10,000 m³/h) – nízká tlaková ztráta snižuje spotřebu energie kompresoru.
- Po proudu (Rafinerie): Kuželové ventily s kovovým sedlem si poradí s těžkým olejem a asfaltem (400° C.) – Zátky z karbidu wolframu odolávají otěru částicemi koksu.
Voda a čištění odpadních vod
- Manipulace s kaly: Excentrické kuželové ventily (měkká sedadla, Třída VI) manipulujte s kalem s 20–30 % pevných látek – žádné ucpávání, 60% kratší prostoje než kulové ventily.
- Dávkování chemikálií: Nemazané kuželkové ventily (Sedadla PTFE) kontrola dávkování chlóru/fluoridu – netěsnost třídy VI zabraňuje kontaminaci vody.
- Odsolování: 316Zátkové ventily L zvládají slanou vodu (538° C.) - zajišťuje odolnost proti korozi 10+ rok životnosti.
Chemický a farmaceutický
- Zpracování kyselin: Rukojeť ventilů Hastelloy C276 98% kyselina sírová (650° C.) - nulová koroze, setká se s ISO 15848-1 Třída AH.
- Léčiva: Kuželové ventily potažené PTFE (ASME BPE) regulovat dávkování API – netěsnost třídy VI a schopnost CIP zabraňují křížové kontaminaci.
Výroba energie
- Tepelné elektrárny: Kuželové ventily s kovovým sedlem řídí přehřátou páru (540° C., 200 bar) – používá se v obtokových systémech turbín.
- Jaderné elektrárny: 316L kuželové ventily s kovovým vlnovcem zvládají borovanou chladicí kapalinu – nulový únik (Třída VI) zabraňuje uvolnění záření.
Těžba a nerosty
- Přeprava kejdy: Excentrické kuželové ventily (sedadla z karbidu wolframu) manipulovat s důlní hlušinou (30% pevné látky) - 300% delší životnost než u kulových kohoutů s pryžovou výstelkou.
- Flotační procesy: Kuželové ventily s pryžovým sedlem řídí chemikálie pro flotaci pěny – nízké náklady a snadná údržba pro vzdálená pracoviště.
10. Srovnání s jinými ventily
Kuželové ventily jsou jedním z několika typů ventilů používaných při řízení průmyslových kapalin.
Pochopení jejich relativních silných stránek a omezení pomáhá konstruktérům vybrat nejvhodnější ventil pro konkrétní aplikaci.
Níže uvedená tabulka porovnává kuželkové ventily s jinými běžně používanými ventily:
| Typ ventilu | Design & Operace | Klíčové výhody | Omezení | Typické aplikace |
| Zástrčný ventil | Otočná válcová nebo kónická zástrčka s portem; čtvrtotáčkový provoz | Jednoduchý, kompaktní, bublinotěsné uzavření; pokles nízkého tlaku; univerzální pro průtok s více porty | Točivý moment ručního ovládání může být u velkých velikostí vysoký; často nutné mazání; omezené škrcení | Kalivy, olej & plyn, chemické technologické linky, odklonění toku, Vzorkování |
| Kulový ventil | Kulovitá koule s vývrtem; Čtvrtletní | Rychlý provoz; bublinotěsné těsnění; dobré pro vysoký tlak/teplotu; nízký točivý moment | Omezené konfigurace s více porty; není ideální pro erozivní média | Voda, plynovody, chemické linky, on/off aplikací |
| Brána ventil | Posuvná brána mezi sedadly; lineární pohyb | Minimální pokles tlaku po plném otevření; obousměrné; vhodné pro velké průměry | Pomalý provoz; Chudák; objemný; potenciální vibrace nebo chvění | Pára, voda, potrubí; izolační povinnosti |
Globe ventil |
Lineární pohyb zástrčka/sedlo nebo kotouč/sedlo; škrtící design | Výborná regulace průtoku; přesná kontrola; robustní těsnění | Vyšší pokles tlaku; Složitější; pomalejší provoz; vyšší náklady | Řízení procesů, Chemické rostliny, výroba energie, škrtící povinnosti |
| Ventil motýlů | Rotující disk; Čtvrtletní | Lehký, kompaktní; mírné škrcení; nákladově efektivní pro velké průměry | Omezená těsnost pod vysokým tlakem; není vhodný pro abrazivní kapaliny | HVAC, úpravy vody, nízkotlaké chemické linky |
| Jehlový ventil | Kuželová jehla a sedlo; lineární pohyb | Jemná regulace průtoku; přesné měření | Ne pro vysoký průtok; pomalý provoz; malá velikost | Instrumentace, Vzorkování, laboratorní aplikace |
Klíčové poznatky:
- Těsnění: Zátkové ventily poskytují bublinotěsné uzavření podobné kulovým ventilům, ale dokážou efektivněji zvládnout vícecestný průtok.
- Schopnost škrcení: Lineární ventily jako kulové a jehlové ventily vynikají přesnou regulací průtoku; kuželkové ventily jsou vhodnější pro zapínání/vypínání a odklonění než pro jemné škrcení.
- Pokles tlaku: Zátkové a kulové kohouty mají nízký Δp v plně otevřených pozicích; kulové a šoupátkové ventily mohou způsobit významný pokles tlaku.
- Údržba a životnost: Mazané kuželkové ventily vyžadují pravidelnou kontrolu v abrazivních nebo korozivních médiích; kuželkové ventily s kovovým sedlem poskytují dlouhodobou spolehlivost v náročných podmínkách.
- Všestrannost: Zátkové ventily s víceportovými konfiguracemi mohou vyměnit několik ventilů v převaděči, mixér, nebo vzorkovací systémy, snížení složitosti potrubí.
11. Závěr
Kuželové ventily jsou robustní, kompaktní čtvrtotáčkové zařízení ideální pro zapnutí/vypnutí, přesměrování a mnoho izolačních povinností.
Jejich výkon závisí na pečlivém výběru podpory zástrčky (Plovoucí vs Trunnion), typ sedadla (kov vs odolný), materiály a ovládání.
Nejsou nejlepší volbou pro přesné škrcení, ale při rychlé akci, je vyžadována jednoduchá konstrukce a robustní manipulace se znečištěnými nebo abrazivními kapalinami, kuželové ventily jsou často nejpraktičtějším řešením.
Moderní materiály, povlaky a digitální aktuátory nadále rozšiřují svou použitelnost.
Vlastní ventilové sestavy od LangHe
Langhe nabídky zakázková řešení montáže ventilů, specializující se na přizpůsobené komponenty pro splnění specifických průmyslových požadavků.
Využití pokročilého odlévání, Přesné obrábění, a materiální expertizy, LangHe poskytuje zátkové ventily, kontrolní ventily, a další ventilové sestavy s:
- Vlastní materiály: Uhlíková ocel, nerez, Duplex, slitiny niklu, a vysoce výkonné materiály pro korozivní nebo vysokoteplotní aplikace.
- Návrhy na míru: Jednoportový, víceportový, namazaný, nebo kuželkové ventily s kovovým sedlem konstruované podle specifikací klienta.
- Přesné obrábění: CNC opracovaná těla a zátky s úzkými tolerancemi pro hladký provoz a nepropustné těsnění.
- Montáž a testování: Plně smontované ventily, hydrostaticky a funkčně testováno, aby splňovalo ISO, API, nebo klientské standardy.
Langhepřizpůsobené služby umožňují průmyslová odvětví, jako je např olej & plyn, Chemické zpracování, úpravy vody, a výroba energie integrovat ventily, které se setkávají unikátní operační, prostorový, a výkonnostní omezení, zajištění spolehlivosti, účinnost, a dlouhá životnost.
Kontaktujte LangHe ještě dnes navrhovat a vyrábět komponenty ventilů na míru přesně podle vašich specifikací.
Časté časté
Jaký je rozdíl mezi kuželkovým a kulovým ventilem?
Kuželové ventily používají válcovou/kuželovou kuželku (excentrické konstrukce snižují opotřebení), zatímco kulové ventily používají kulovou kouli.
Kuželové ventily vynikají v abrazivních/korozivních kapalinách (300% delší životnost v kalech), zatímco kulové kohouty jsou levnější pro neabrazivní, aplikace s vysokým průtokem.
Jaký typ kuželového ventilu je nejlepší pro abrazivní kaly?
Excentrické kuželkové ventily se sedlem z karbidu wolframu (85– 90 HRC) jsou nejlepší.
Excentrický design zvedá zástrčku ze sedla (žádný kluzný kontakt), a karbid wolframu odolává opotřebení pevnými látkami – prodlužuje životnost na 1–2 roky vs. 3– 6 měsíců pro kulové kohouty.
Jak často by se měly mazané kuželkové ventily mazat?
Čtvrtletně za normálního provozu (olej & plyn, voda); měsíčně pro abrazivní kapaliny (hornictví). Automatické mazací systémy (pneumatické vstřikovače) může prodloužit intervaly na 6–12 měsíců.
Umí uzavírací ventily zvládnout vysoké teploty?
Ano. Kuželové ventily s kovovým sedlem (Stellite 6, Hastelloy C276) zvládnou až 815°C (jaderných/elektráren). Ventily s měkkým sedlem (PTFE) jsou omezeny na 260°C.
Jaká je třída úniku kuželkových ventilů?
Kuželové ventily s měkkým sedlem (PTFE/Viton) dosáhnout ANSI FCI 70-2 Třída VI (≤ 0,00001 % únik) – kritické pro toxické/drahé kapaliny.
Ventily s kovovým sedlem dosahují třídy IV (≤ 0,01 % únik) – vhodné pro provoz při vysokých teplotách.
Jak mohu snížit požadavky na krouticí moment pro kuželkové ventily?
Používejte mazané zátky (grafit-PTFE mazivo snižuje tření o 50%); vyberte excentrické vzory (zvedne zástrčku ze sedadla); zajistěte správné vyrovnání potrubí (vyhýbá se vazbě).


